An uncommon but not to be missed injury
Here Dr Branson gives a medical summary with literature review on an unusual but not to be missed cause for persisting ankle pain in athletes.
Dr Branson sees all injuries related to sport and has a specialist interest in tendon injuries and joint preservation. To Book an appointment call 1300 858 856.
Incidence:
Medial malleolar stress fractures are relatively uncommon 0.6-4.1% of all stress fractures1 but can cause significant morbidity and lost game time. These fractures occur in runners and running sports and are more common in skeletally mature athletes
Clinical presentation:
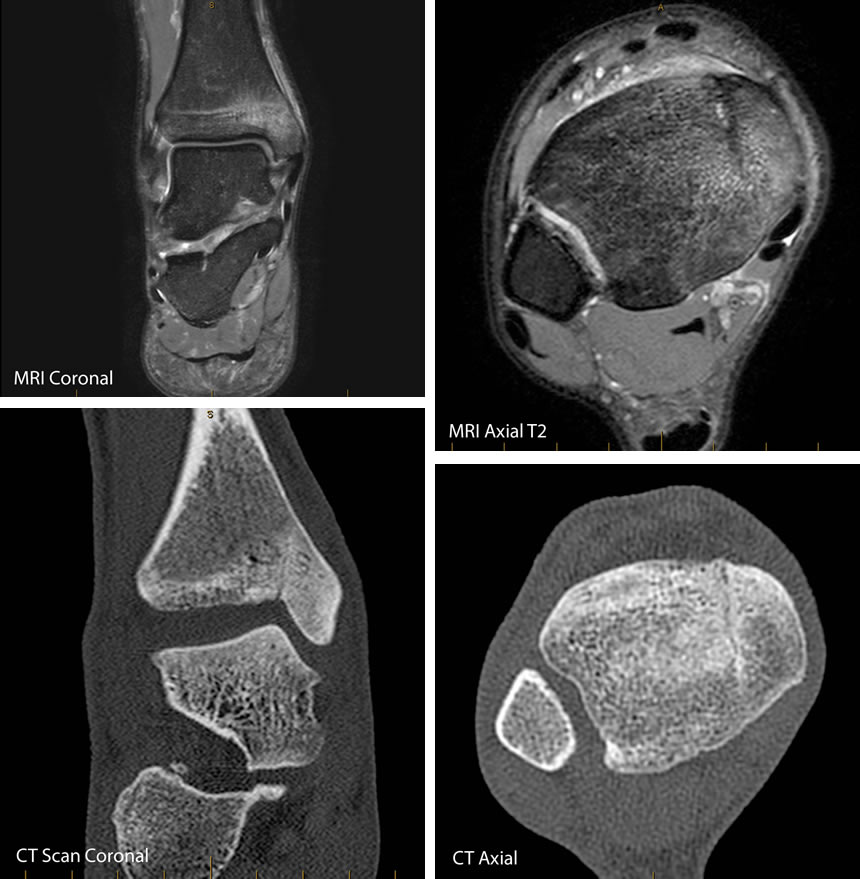
Stress fractures of the medial malleolus (Inside part of the ankle – see diagram) should be suspected in patients involved in athletic and running sports who have experienced persistent and unexplained pain over the medial malleolus.
In football codes there may be an association between medial malleolar stress fractures and anterior ankle impingement with one theory being that the stress fracture may be the end stage of chronic anteromedial ankle impingement secondary to spurs2. There should be a high index of suspicion in worsening symptoms of anterior impingement with medial malleolar pain.
The fracture line is usually runs vertical from the tibial plafond, although may run obliquely through the medial malleolus and may extend to the external cortical surface3.
Medial malleolar fractures are inherently unstable and prone to non-union. They should therefore be considered a high risk stress fracture.
Investigation
Medial malleolar stress fractures are generally not visible on Xrays. MRI scans have a high sensitivity and high specificity for bone stress4,5. CT scans may be needed to further evaluate the full extent of the fracture line and assess cortical bone.
Medial malleolar stress fractures with no fracture line visible on Xray or CT may be treated with aggressive immobilisation (strict non weight bearing / immobilization below knee cast or boot for 4- 6 weeks).
Stress fractures with a fracture line demonstrated on X-ray or CT require surgical intervention - open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). This remains the treatment of choice as healing can take up to 8 months with conservative treatment 6,7. In elite athletes ORIF can lead to early recovery and return to sport 6,7,8,9. Anterior ankle impingement should be treated at the same time.
“The key to diagnosing and treating medial malleolar stress fractures appropriately is a high index of suspicion and careful clinical examination looking for bony tenderness on the medial malleolus.”
References
1. Michel P.J. et al: Treatment of Medial Malleolar Stress Fractures
Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine
April 2009Volume 17, Issue 2, Pages 106–111
2.Jowett AJ, Birks CL, Blackney MC: Medial malleolar stress fracture secondary to chronic ankle impingement. Foot Ankle Int. 2008 Jul;29(7):716-21.
3. Peter Brukner, MBBS; Chris Bradshaw, MBBS; Kim Bennell, PhD: Managing Common Stress Fractures: Let Risk Level Guide Treatment
The Physician and Sports Medicine. 1998,Volume 26 ,No 8.
4.Schils JP1, Andrish JT, Piraino DW, Belhobek GH, Richmond BJ, Bergfeld JA.: Medial malleolar stress fractures in seven patients: review of the clinical and imaging features.
Radiology. 1992 Oct;185(1):219-21.
5. 10. Krestan CR, Nemec U, Nemec S. Imaging of insufficiency fractures. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2011;15:198–207.
6.S. Orava, et.al.: Stress Fracture of the Medial Malleolus; J. of Bone and Joint Surg., 1995; 77-A(3): 362-365.
7.K. Shelborne, et.al.: Stress Fractures of the Medial Malleolus; Am. J. of Sports Med., 1988; 16: 60-63.
8.Shabat S1 et al: Stress fractures of the medial malleolus--review of the literature and report of a 15-year-old elite gymnast, Foot Ankle Int. 2002 Jul;23(7):647-50
9.Donley B, LLaslan H: Stress Fractures of the Medial Malleolus; Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine, 2006; 14 :4 : 252-258